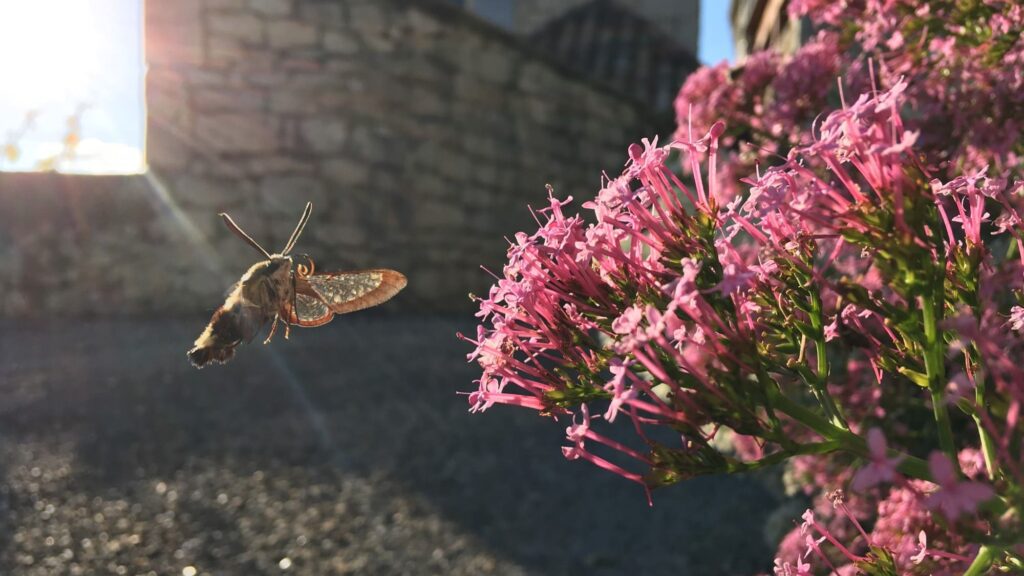
Faced with the challenges of food security, agroecological transition, and climate change, the issue of crop yields is more important than ever. Producing more, of course, but above all producing better: with limited resources, in often constrained contexts, and while maintaining crop quality.
Here you will find clear and concrete insights into agricultural yield: its definition, the factors that influence it, the levers for optimization, and the role that biostimulants can play in sustainably improving agricultural performance.
Agricultural yield: key data for understanding it
Agricultural yield is a fundamental indicator for assessing the efficiency of a crop. It should not be confused with total production, but rather serves to measure performance on a given area.
What is the difference between yield and production?
Agricultural production corresponds to the total volume harvested on a plot of land, a farm, or a territory. Yield, on the other hand, is expressed per unit of area: tons per hectare, quintals per hectare, or kilograms per square meter in France, depending on the crop. In other countries, such as the United States, other units are used, such as bushels per acre or pounds per acre. In all cases, yield allows for an objective comparison of the efficiency of a cropping system.
How is agricultural yield calculated?
The calculation is simple: Yield = Quantity harvested ÷ Area cultivated
For example, 6,000 kilograms of potatoes harvested from 1 hectare gives a yield of 6 tons per hectare (t/ha).
What is yield used for?
Agricultural yield makes it possible to identify areas for improvement, compare seasons, and adjust technical practices. It is therefore central to the agronomic and economic management of farms.
What are the main factors influencing crop yields?
Crop yields are the result of a complex combination of agronomic, environmental, and technical factors. Understanding how these factors interact is essential for identifying the levers for improvement that are appropriate for each crop and each soil and climate context.
The following are the main factors that directly or indirectly influence crop yields:
Soil quality: structure, organic matter, water retention capacity, biological activity, etc. Living soil is the basis for good crop performance.

Plant nutrition: a balanced supply of nutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, trace elements) is essential to support growth.

Climatic conditions: temperature, rainfall, sunshine, and extreme events (frost, heat waves, hail) have a direct impact on crop development.

Water management: irrigation or natural rainfall strongly influence yield, especially during periods of water stress.
Plant material used: variety selection, certified or uncertified seeds, adaptability to local conditions.

Cultivation practices: sowing density, crop rotation, weeding, tillage, etc.
Added to these factors are biotic pressures (diseases, pests) and abiotic pressures (drought, salinity, heat), which are becoming increasingly frequent.
How can agricultural yields be improved without compromising sustainability?
Improving agricultural yields does not necessarily mean increasing inputs. On the contrary, agricultural sectors are increasingly turning to technical solutions that optimize resources and limit environmental impact. The objective is no longer solely quantitative, but also qualitative and sustainable.
Among the most effective levers are: rational management of inputs (fertilization, irrigation), the implementation of diversified crop rotations, permanent soil cover, and the use of conservation practices such as direct seeding or no-till farming. These agroecological approaches help maintain soil fertility while reducing dependence on phytosanitary products.
Success also requires careful adaptation to soil and climate conditions, with increasingly precise crop management, whether for perennial crops, market gardening and horticulture, or field crops and plantations. Sensors, decision-making tools, regular analyses, etc. The combination of field observation and technical innovation now makes it possible to envisage high-performance agriculture that is more resilient to climate change and better equipped to meet food security challenges.
Biostimulants: a lever for improving crop quality and yield
Biostimulants are now establishing themselves as technical tools in their own right, helping farmers to improve their yields. Unlike fertilizers or plant protection products, they do not act directly on plant nutrition or protection, but on their physiology, by stimulating their natural functions.
Used as part of a sustainable agronomic strategy, biostimulants can strengthen root development, improve nutrient assimilation, increase tolerance to abiotic stress (drought, heat, salinity, etc.), and optimize plant vigor at key stages. They also contribute to greater crop uniformity, better fruit or vegetable size, and improved visual quality after harvest.
Regardless of their composition, biostimulants are part of a sustainable and technical approach. By mobilizing the biological potential of plants, they enable agriculture that is both efficient and more resilient to hazards, and better aligned with societal expectations in terms of sustainability.

Produce better and sustainably with biostimulants
To improve your yields without compromising the sustainability of your practices, biostimulants offer concrete and proven solutions. By stimulating the natural functions of plants, they enable you to increase efficiency, quality, and resilience. Explore their potential and integrate them into your technical itineraries to cultivate with performance, responsibility, and confidence in the future.


